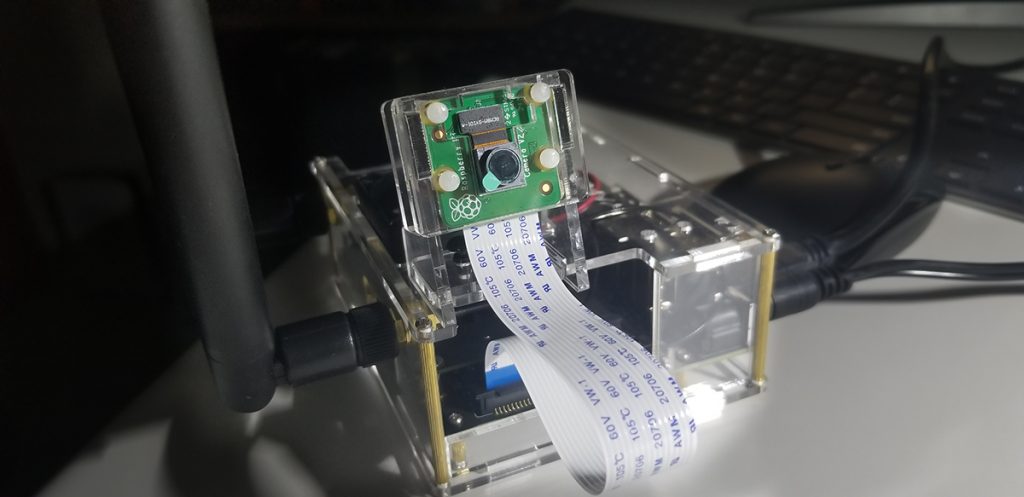
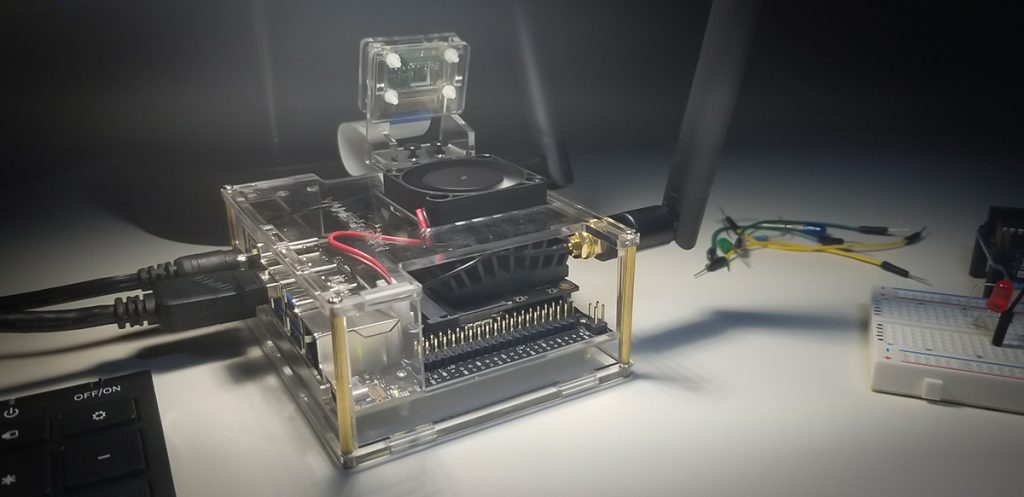
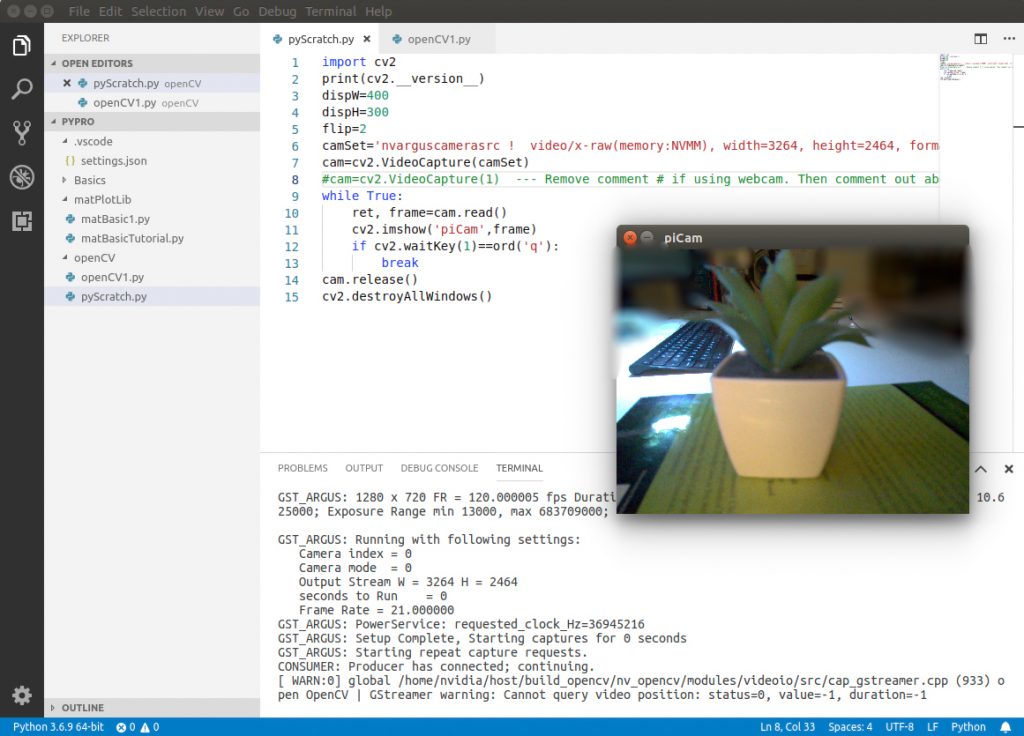
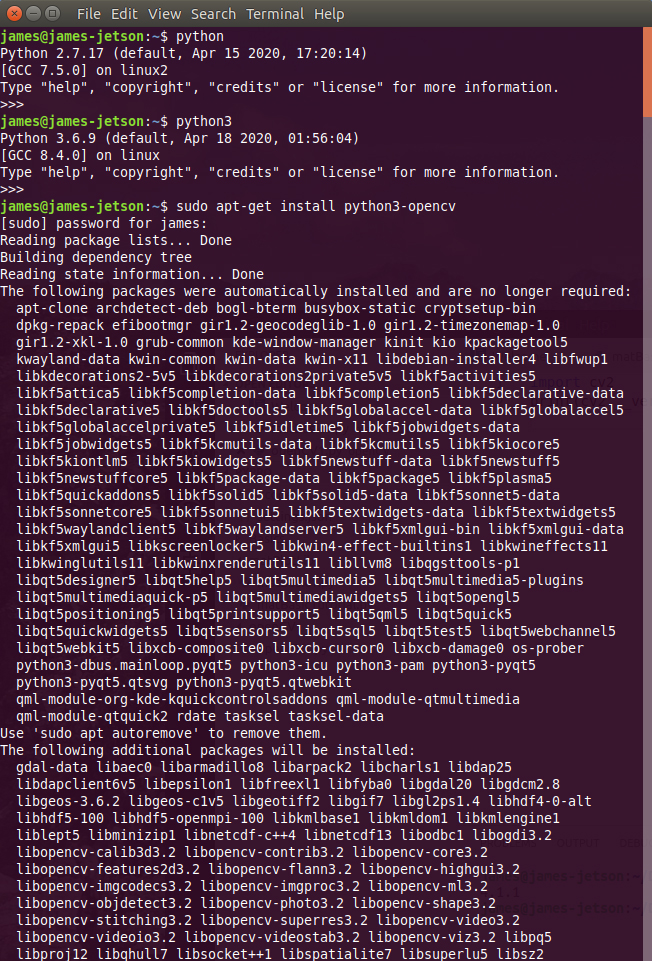
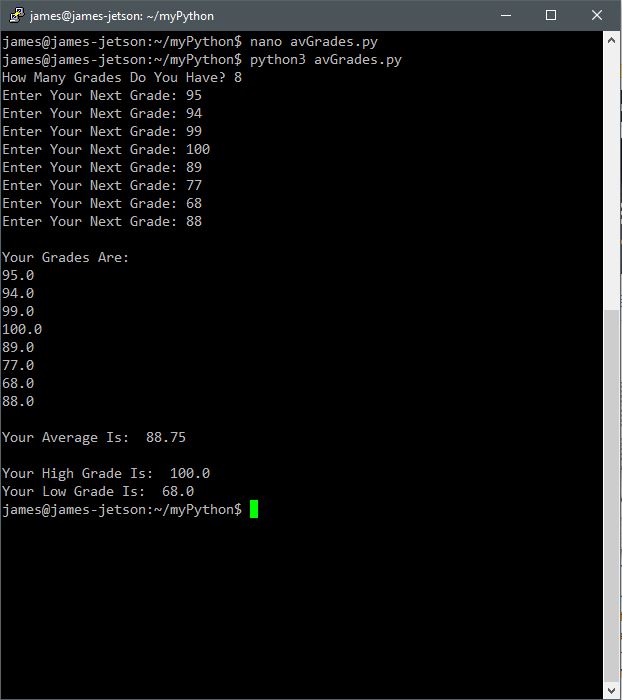
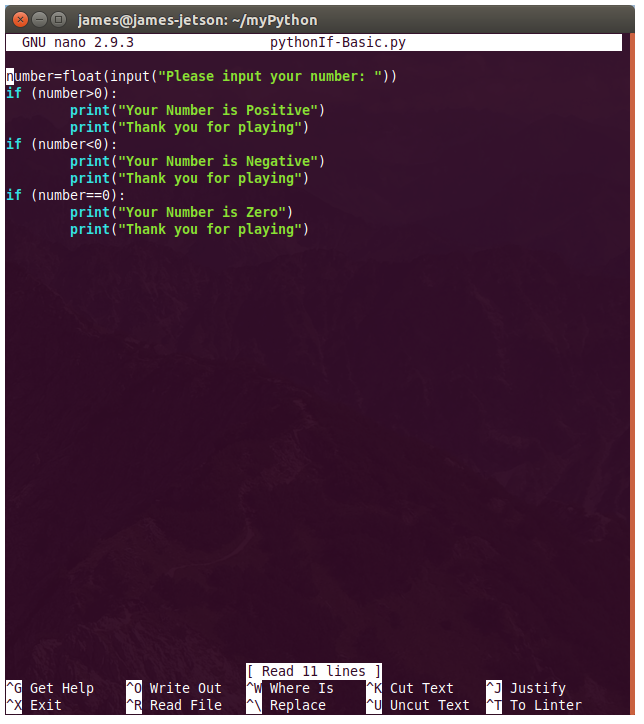
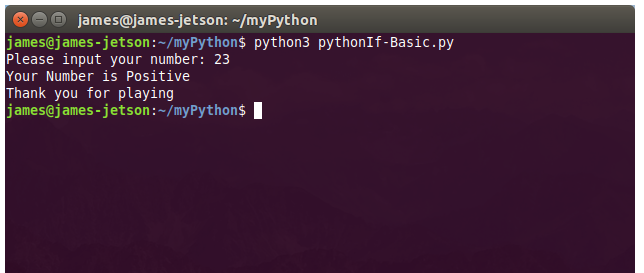
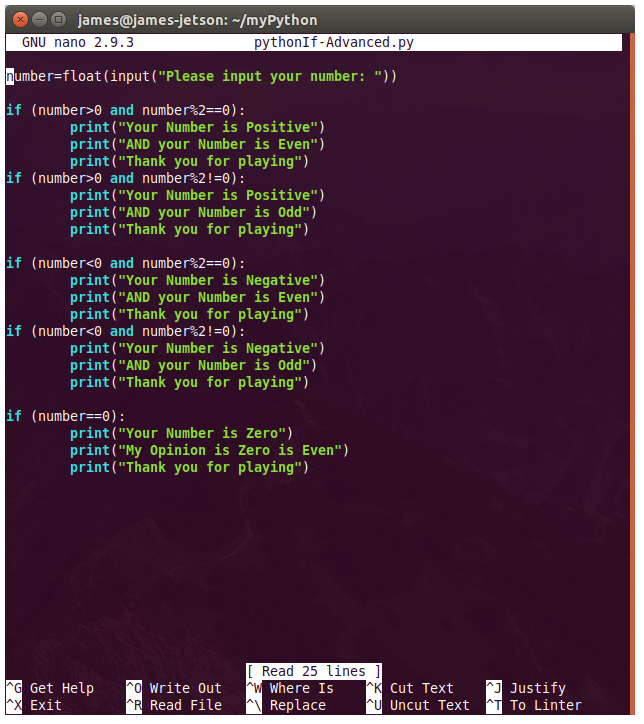
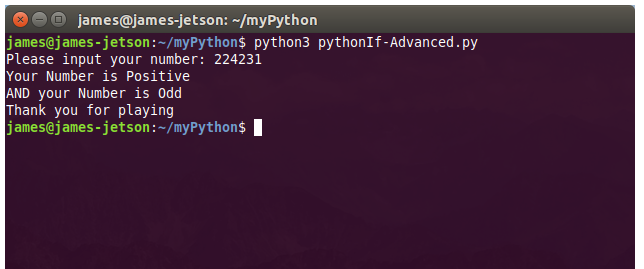
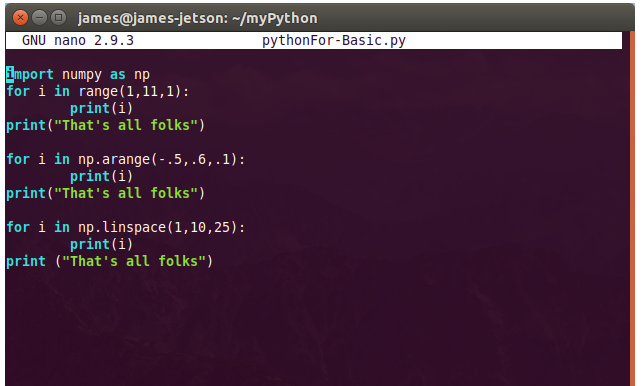
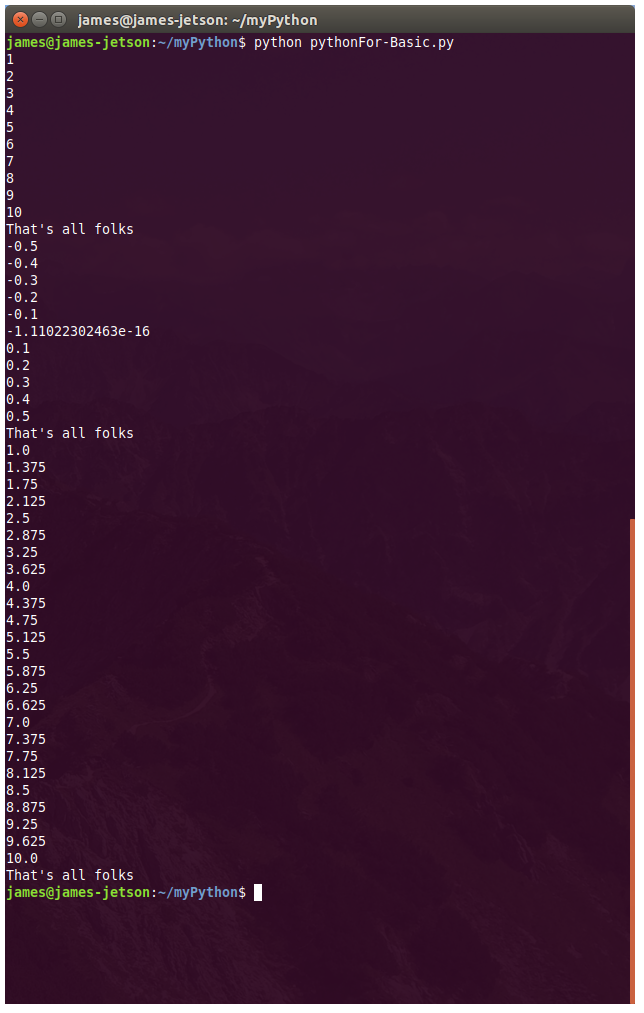
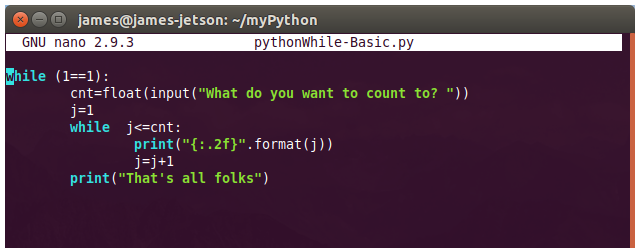
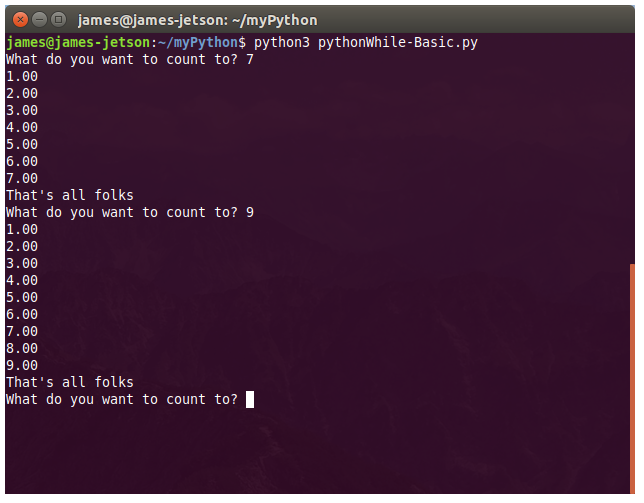
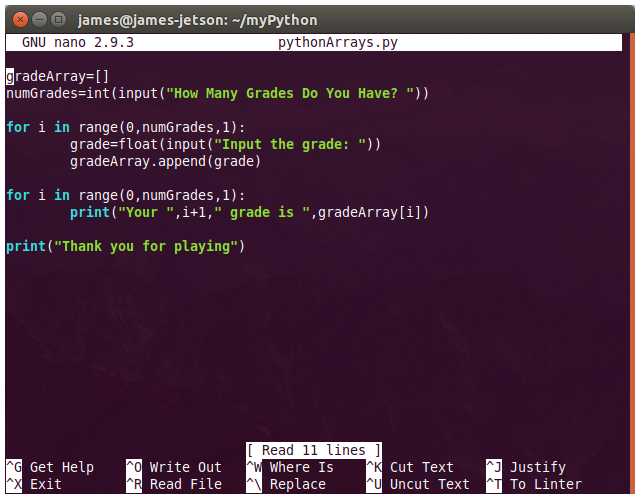
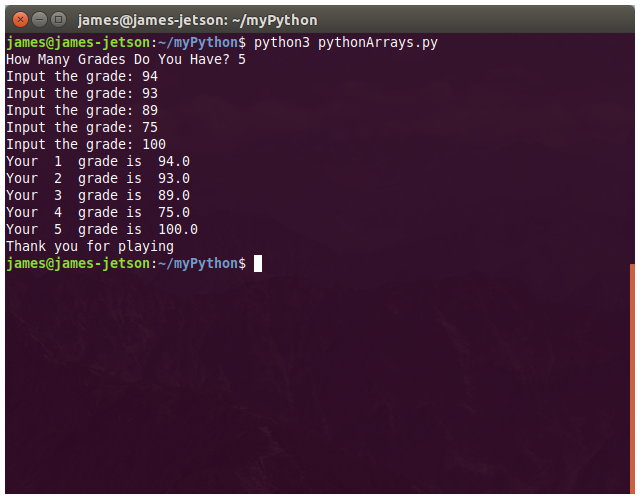
There are numerous configuration requirements involved in the setup and operation of the Jetson unit to produce relevant AI related projects. To support meaningful project activity, these are the steps to go through. Much of this effort
- Install and update Linux
- Install Visual Studio Code IDE
- Install Python 3 using VS Code IDE
- Install Code Interpreter
- Install and update openCV library for AI applications
- Install Numpy library for numerical function support
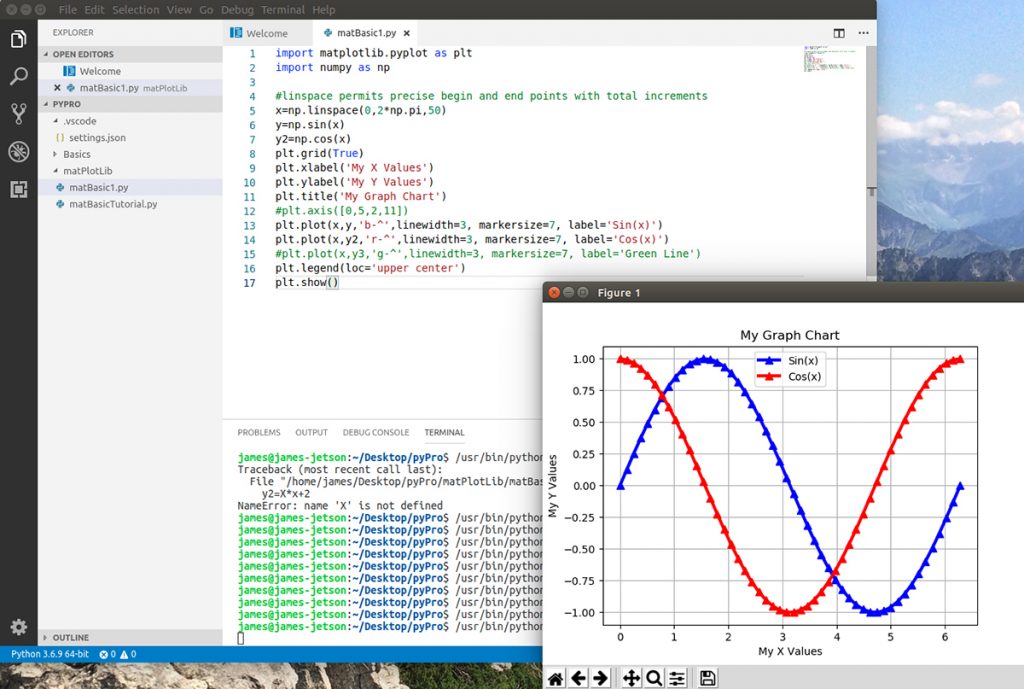
- Install MatPltLib to plot mathematical operations and arrays
Upon completion of the setup walk-through, the short initialization program is necessary to get the camera operating. This initialization code adds libraries and configures the camera with settings unique to its resolution limits or parameters.